002 – Apr 8, 2025
One State, One RRB: Merging Roots for Rural Financial Strength 🏦

🧭 Thematic Focus
Category: Banking & Financial Sector Reforms | Rural Development | Governance
GS Paper: GS Paper III – Indian Economy | Inclusive Growth
Tagline: When small streams unite, a stronger current reaches the village.
🧾 Intro
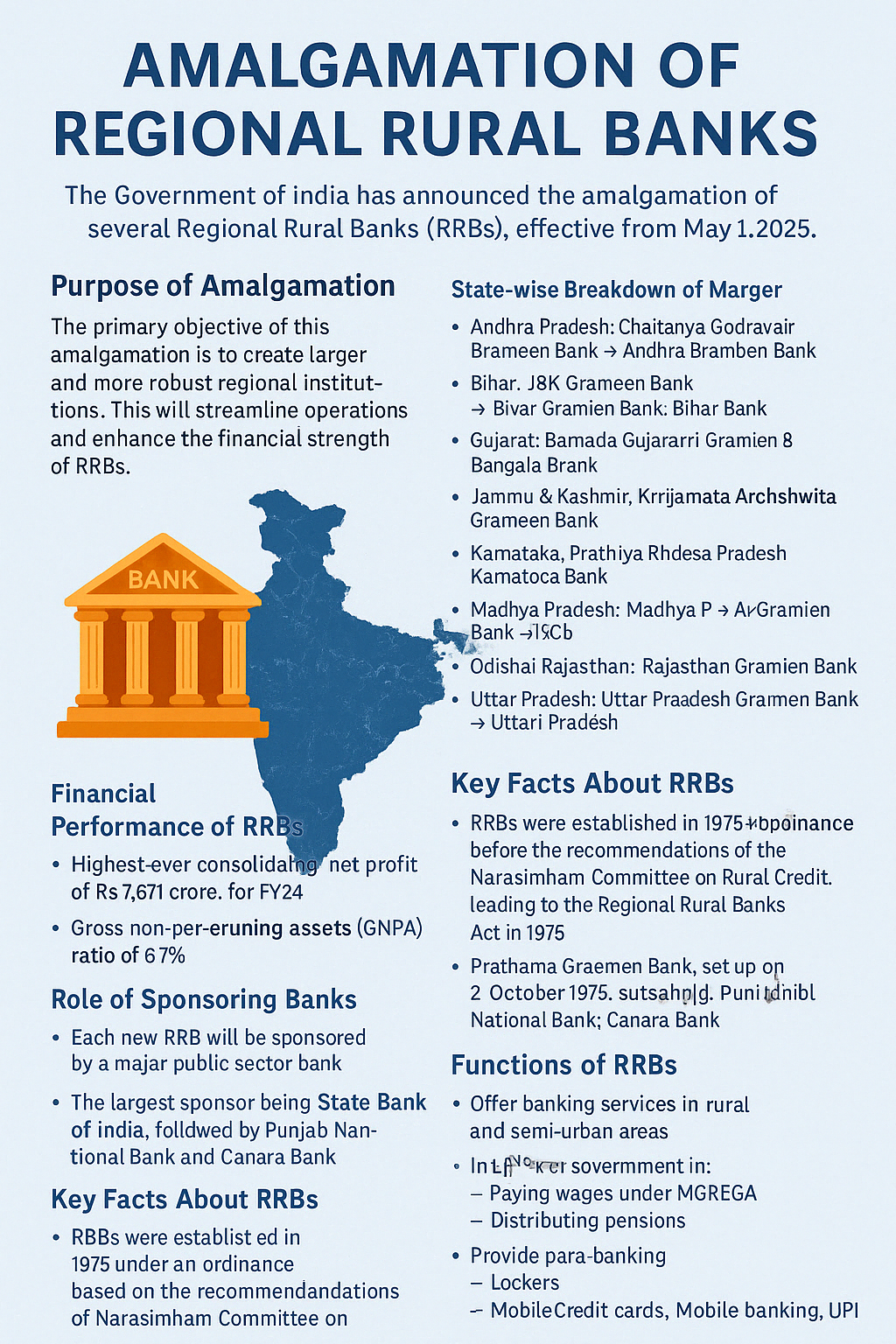
In a transformative stride towards financial efficiency and rural empowerment, the Government of India has announced the amalgamation of multiple Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) across states, effective May 1, 2025.
This is the operational rollout of the One State, One RRB Policy, announced by the Finance Ministry in September 2024, marking a new era in rural banking consolidation.
🔍 Key Highlights
🧩 Purpose of Amalgamation
- Create larger, robust rural banks
- Reduce intra-public sector competition
- Improve credit flow and operational efficiency
- Strengthen service delivery in rural India
🗺️ State-wise Merger Plan
| State | Merged Entity |
|---|---|
| Andhra Pradesh | Andhra Pradesh Grameena Bank |
| Bihar | Bihar Gramin Bank |
| Gujarat | Gujarat Gramin Bank |
| Jammu & Kashmir | Jammu & Kashmir Grameen Bank |
| Karnataka | Karnataka Grameena Bank |
| Madhya Pradesh | M.P. Gramin Bank |
| Maharashtra | Maharashtra Gramin Bank |
| Odisha | Odisha Grameen Bank |
| Rajasthan | Rajasthan Gramin Bank |
| Uttar Pradesh | Uttar Pradesh Gramin Bank |
| West Bengal | West Bengal Gramin Bank |
📈 Financial Performance (FY24):
- Net Profit: ₹7,571 crore – highest ever
- GNPA Ratio: 6.1% – lowest in a decade
- Reflects operational maturity and profitability
🏛️ Sponsoring Banks – Backbone of Stability
- State Bank of India – Largest RRB sponsor
- Followed by Punjab National Bank and Canara Bank
- Sponsoring banks provide capital, systems, and support
📜 Know Your RRBs: Origins & Structure
- Established in 1975 (Ordinance), formalised in 1976
- First RRB: Prathama Grameen Bank (Oct 2, 1975)
- First sponsor: Syndicate Bank
- Ownership pattern:
- 50% – Central Govt
- 35% – Sponsor Bank
- 15% – State Govt
🧺 Functions of RRBs:
- Provide banking in rural/semi-urban areas
- Help with MGNREGA payments, pensions
- Offer para-banking services: UPI, mobile banking, lockers, cards
🧠 Concept Explainer: Why This Matters
Small institutions face high overheads and fragmented delivery.
This consolidation brings scale, eases integration of digital services, and prepares RRBs to be pillars of rural credit and social security delivery.
In an age of financial technology, this policy aligns tradition with systemic strength.
🗺️ GS Paper Mapping
- GS Paper III – Banking Reforms | Rural Credit and Financial Inclusion
- GS Paper II – Governance & Policy Execution at Grassroots
- Essay Themes – “Inclusive Growth with Structural Reform,” “Banking the Unbanked”
💭 A Thought Spark — by IAS Monk
“When rural roots intertwine through trust,
even the smallest bank branch becomes a bridge to prosperity.”