🧭June 11, 2025 Post 2: India’s Services Exports Hit Record High in May 2025 | High Quality Mains Essay | Prelims MCQs
India’s Services Exports Hit Record High in May 2025

NATIONAL
📅 Post Date: June 11, 2025
📘 Thematic Focus: Economy | External Sector | Trade Growth
🌿 Opening Whisper
“When knowledge travels without borders, prosperity finds a new language.”
“In the mosaic of global trade, it’s India’s services that are painting the boldest strokes.”
🔍 Key Highlights
- India’s services exports surged to a record $32.8 billion in May 2025 — a 12.7% YoY growth compared to May 2024.
- The Information Technology (IT) and Business Process Management (BPM) sectors led the growth, contributing over 55% of total services exports.
- Top export markets: United States, UK, EU, and UAE remain major destinations.
- Sectors showing robust growth: Financial services, software development, legal outsourcing, design, animation, and consultancy.
- The India Brand Equity Foundation (IBEF) and Commerce Ministry emphasized the role of digital infrastructure, talent pool, and new Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) in driving this boom.
📘 Concept Explainer: What Makes India’s Services Sector Unique?
- India’s services sector contributes over 50% of GDP and employs a large segment of urban skilled workforce.
- Highly educated English-speaking professionals, robust telecom infrastructure, and a globally competitive cost structure give India an edge.
- Mode 1 (Cross-border) and Mode 4 (movement of professionals) are key in India’s WTO services profile.
📘 Concept Explainer: What Powers the Services Boom?
Economic multiplier: High export income supports GDP, strengthens the rupee, and creates quality urban jobs.
Global competitiveness: India’s large, English-speaking, digitally skilled workforce at competitive costs.
Services diversity: Beyond IT/BPM, export offerings now include financial consulting, legal services, design, animation, and travel.
Policy tailwinds: New FTAs (e.g., India–UK) and improved digital infrastructure are strengthening market access
🧭 GS Mains Mapping
- GS Paper 3 – Indian Economy | External Sector | Services Trade
- GS Paper 2 – International Relations (India’s soft power through IT diplomacy)
💭 A Thought Spark — by IAS Monk
“India’s software code has quietly become the grammar of the global economy. What began with back-offices has now evolved into brain-offices. It is not just exports we trade, but trust — in our minds, in our skills, and in the silence of an engineer’s logic.”
💭 A Thought Spark — by IAS Monk
“As the world outsourced its code and creativity, India didn’t just fill orders—it became the architect of trust, turning ones and zeros into bridges between continents.”
High Quality Mains Essay For Practice :
Word Limit 1000-1200
India’s Services Export Boom: Powering a New Era of Global Trade Leadership
Introduction
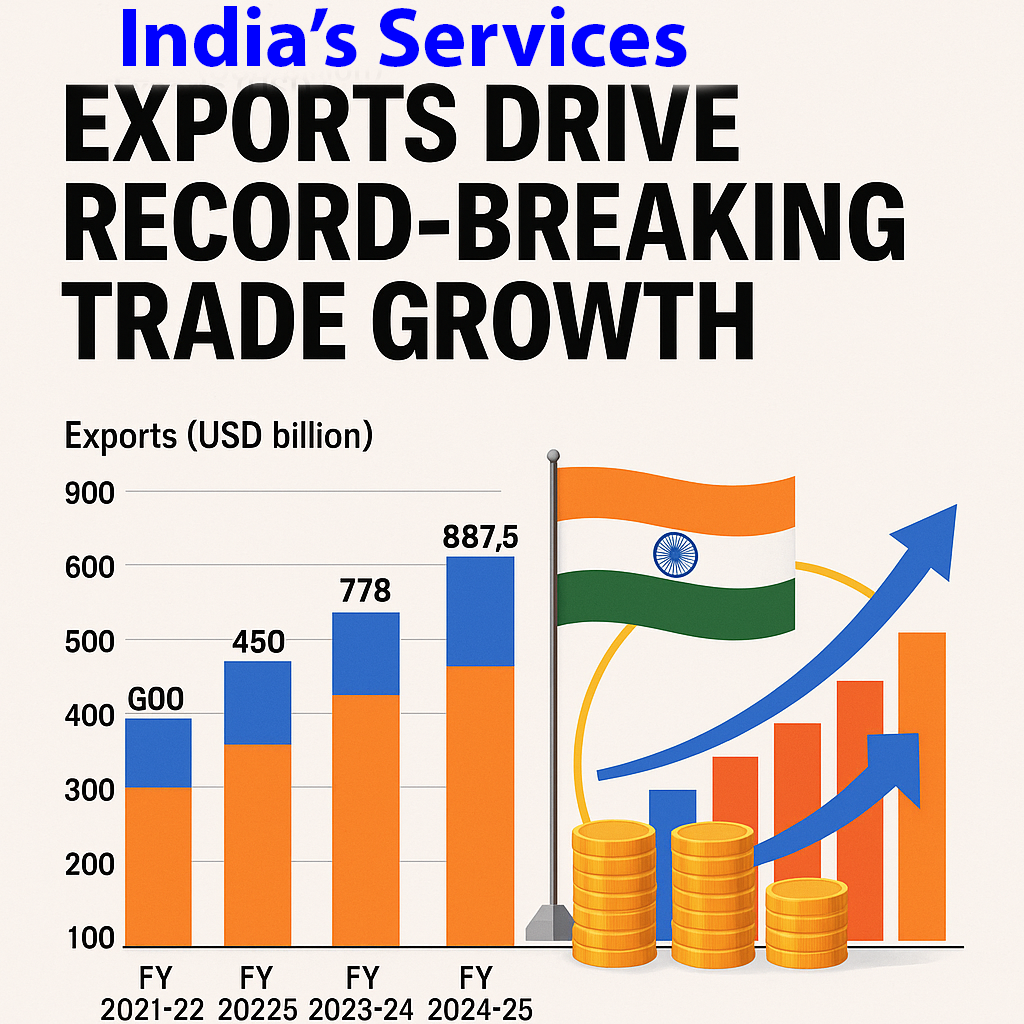
India’s journey as a global services powerhouse has taken a decisive leap forward. In FY 2024–25, India’s services exports reached an all-time high of USD 387.5 billion, contributing significantly to the country’s total exports of USD 887.5 billion. This performance not only reflects India’s comparative advantage in knowledge-intensive services but also marks a structural shift in the architecture of global trade. With the IT sector, professional consulting, financial services, and creative industries leading the charge, India’s services sector has become the new engine of economic diplomacy, employment, and soft power projection.
Historical Context: From Back-Office to Global Brain-Trust
India’s rise in the services trade ecosystem is not an overnight miracle. It is the outcome of decades of policy support, demographic advantage, digital infrastructure growth, and global trust in Indian professionals. Since the 1990s, India’s liberalization reforms opened the floodgates for global IT outsourcing. Companies like Infosys, TCS, and Wipro became global brands, while cities like Bengaluru emerged as global tech hubs.
By the mid-2000s, India’s BPM (Business Process Management) and ITES (Information Technology Enabled Services) dominated back-office support worldwide. However, the current boom is more than just a continuation—it represents a transition from execution support to strategic innovation.
Key Drivers Behind the Current Boom
1. Expanding the Services Basket
While IT services remain the backbone, there is now an expanded and diversified services portfolio.
- Financial services (especially fintech, insurance, compliance analytics)
- Legal process outsourcing
- Design and animation
- Tourism and hospitality services (revived post-COVID)
- Telecommunication and cloud computing solutions
This diversification has reduced sectoral vulnerability and widened India’s global footprint.
2. Digital Infrastructure & Start-up Ecosystem
The growth of Digital India, along with platforms like UPI, Aadhaar, and ONDC, has built a domestic foundation that supports outward exports.
India now boasts over 100 unicorns, many offering SaaS (Software as a Service) platforms globally. With rising demand for cybersecurity, remote work systems, AI integration, and platform solutions, Indian firms are well-positioned to tap into niche global demands.
3. Skilled Workforce and Language Edge
India’s large, English-speaking, tech-savvy youth population continues to be a strategic advantage. Each year, over 1.5 million engineers and hundreds of thousands of graduates in commerce and law enter the job market. Unlike many other developing nations, India combines scale with professional depth.
4. Improved Trade Diplomacy
New Free Trade Agreements (FTAs), such as India–UAE CEPA and India–Australia ECTA, have improved market access for Indian service providers. Upcoming negotiations with the EU, UK, and Canada aim to unlock more opportunities in consulting, education, and digital commerce.
Recent Trends and Figures
- FY 2024–25: Services exports hit USD 387.5 billion, a 13.6% YoY increase.
- March 2025: Monthly services exports touched USD 35.6 billion, the highest ever recorded.
- PMI (Purchasing Managers Index) for Services stood at 58.8 in May 2025, indicating robust demand and strong job creation in the sector.
The World Bank and WTO have also acknowledged India’s rise as a top 5 global exporter in digitally delivered services.
Strategic Implications for India
A. Boosting the Balance of Payments
India’s merchandise trade balance remains in deficit due to oil and electronics imports. However, a robust services surplus helps stabilize the current account, reduces currency volatility, and attracts foreign exchange.
B. Job Creation in Urban Hubs
While manufacturing faces capital and land constraints, services create high-value urban employment. Cities like Pune, Hyderabad, and Chennai are now witnessing a boom in co-working spaces, gig contracts, and tech startups driven by export-linked demand.
C. Soft Power & Global Influence
India’s services exports are not just about dollars—they symbolize trust, reliability, and global integration. Indian lawyers handle U.S. litigation support. Indian doctors offer remote telemedicine to Africa. Indian ed-tech firms provide training to Southeast Asia. This has transformed India’s image from a peripheral supplier to a central global partner.
Challenges in Sustaining Momentum
Despite the optimism, several bottlenecks remain:
1. Visa and Mobility Barriers
Mode 4 services—movement of natural persons—continues to face resistance in Western markets. Stricter immigration norms limit the potential of Indian professionals abroad.
2. Digital Trade Barriers
Many nations are imposing data localization and digital tax regimes. These could reduce the profitability and compliance ease for Indian exporters.
3. Skill-Quality Mismatch
While India produces graduates in large numbers, only a fraction is industry-ready. Reskilling in AI, blockchain, cloud, and cross-cultural communication is urgently needed.
4. Global Headwinds
Recession fears in the U.S., slow growth in Europe, and geopolitical tensions in the Red Sea and Taiwan Strait can disrupt global demand.
Way Forward
A. Invest in Skilling for Emerging Services
The National Education Policy (NEP) and Skill India programs must realign with export demands. AI trainers, climate consultants, global tax experts, and legal professionals will lead future growth.
B. Push for Services in FTAs
India must aggressively negotiate mutual recognition agreements, digital trade liberalization, and cross-border professional mobility in upcoming trade deals.
C. Brand India Services
A global campaign akin to “Make in India” is needed—“Serve from India”—highlighting Indian trust, innovation, and cultural empathy.
D. Strengthen Data and Privacy Infrastructure
With the new Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA) in place, India must show global clients that their data is secure and privacy-compliant.
Conclusion
India’s services sector is no longer a quiet contributor; it is a strategic pillar of the nation’s global identity and economic resilience. From code to consulting, design to data analytics, India’s exports are shaping boardrooms, courtrooms, classrooms, and hospital rooms across the globe. To sustain this momentum, India must remain agile, upskill relentlessly, and diplomatically push for fairer global trade rules. As the world digitizes, India is not merely exporting services—it is exporting certainty, creativity, and a cultural bridge to the future.
Target IAS-26: Daily MCQs :
📌 Prelims Practice MCQs
Topic:
MCQ 1 – Type 1: How many of the above statements are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding India’s Services Export Performance in FY 2024–25:
1. India’s services exports crossed USD 400 billion for the first time in FY 2024–25.
2. The IT-BPM sector alone accounted for more than half of India’s total services exports.
3. India’s services exports have shown consistent annual decline due to global recessionary trends.
4. The HSBC Services PMI for May 2025 was above 55, indicating expansion in the sector.
How many of the above statements are correct?
A) Only two
B) Only three
C) All four
D) Only one
🌀 Didn’t get it? Click here (▸) for the Correct Answer & Explanation
✅ Correct Answer: A) Only two
🧠 Explanation:
•1) ❌ False – India’s services exports reached USD 387.5 billion, not over 400 billion.
•2) ✅ True – The IT-BPM sector contributed over 50% of total services exports.
•3) ❌ False – Services exports grew 13.6% YoY, not a decline.
•4) ✅ True – The HSBC Services PMI was 58.8, indicating strong expansion.
MCQ 2 – Type 2: Two Statements Based
Consider the following two statements:
1. The India–UK FTA has already been signed and is fully operational, enhancing services exports.
2. India is among the top five global exporters of digitally delivered services, as recognized by the WTO.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A) Only 1 is correct
B) Only 2 is correct
C) Both are correct
D) Neither is correct
🌀 Didn’t get it? Click here (▸) for the Correct Answer & Explanation
✅ Correct Answer: B) Only 2 is correct
🧠 Explanation:
•1) ❌ False – The India–UK FTA is still under negotiation and not yet finalized.
•2) ✅ True – WTO has recognized India as a top-five exporter of digitally delivered services.
MCQ 3 – Type 3: Which of the statements is/are correct?
Which of the following statements correctly explain why India’s services sector is globally competitive?
1. India has a large pool of English-speaking, digitally skilled professionals.
2. Services trade is not affected by visa or cross-border data flow restrictions.
3. Indian IT companies have invested heavily in AI and cloud-based solutions.
4. Urban infrastructure in Tier 1 cities supports high-value service delivery.
Select the correct answer using the code below:
A) 1, 3 and 4 only
B) 2 and 4 only
C) 1 and 2 only
D) 1, 2, 3 and 4
🌀 Didn’t get it? Click here (▸) for the Correct Answer & Explanation
✅ Correct Answer: A) 1, 3 and 4 only
🧠 Explanation:
•1) ✅ True – This is a primary strength of India’s service ecosystem.
•2) ❌ False – Visa/data restrictions are a challenge, not an advantage.
•3) ✅ True – Indian companies are actively adapting to emerging tech.
•4) ✅ True – Urban tech parks, SEZs and metros support exports.
MCQ 4 – Type 4: Direct Fact
What was the total value of India’s services exports in FY 2024–25, as per official data?
A) USD 450 billion
B) USD 387.5 billion
C) USD 312 billion
D) USD 520 billion
🌀 Didn’t get it? Click here (▸) for the Correct Answer & Explanation.
✅ Correct Answer: B) USD 387.5 billion
🧠 Explanation:
••India’s services exports hit a record high of approximately USD 387.5 billion in FY 2024–25, contributing nearly 44% of total exports.















